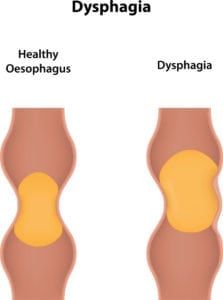
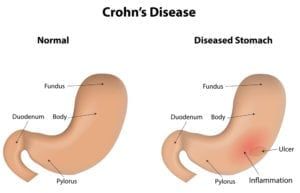
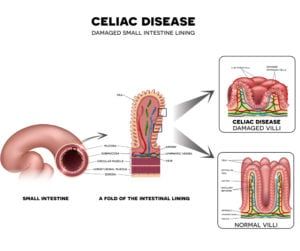
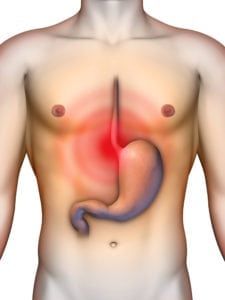
Childhood abdominal pain is an uncomfortable and sometimes debilitating condition that may indicate the presence of an underlying health condition. The pain may be acute, occurring suddenly and lasting a week or less, or it may be chronic, lasting for long periods of time or on a chronic basis. There are a variety of problems that may cause abdominal pain children, and treatment typically varies accordingly.
Did you know…
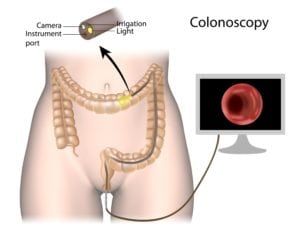
that abdominal pain is responsible for nearly 1 in 20 pediatric visits? School-age children often complain of abdominal pain. While many of those patients are successfully treated by a primary care provider, some are referred to pediatric gastroenterologists for further testing and treatment. Acute and chronic abdominal pain is responsible for approximately 1 in 3 visits to a pediatric GI specialist.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some of the most common causes of pediatric abdominal pain?
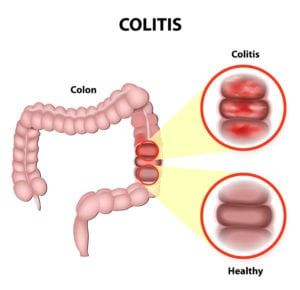
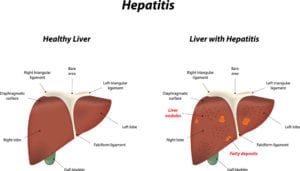
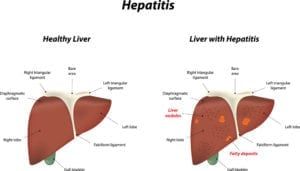
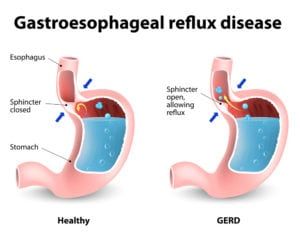
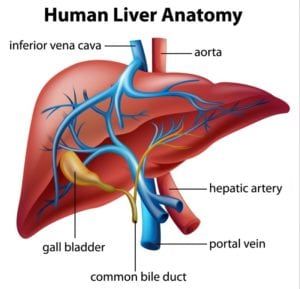
A child’s abdominal pain is often related to an infection or a minor condition such as constipation. Less commonly, abdominal pain may be caused by diseases and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, such as irritable bowel disease, celiac disease or food intolerance.
What symptoms typically accompany childhood abdominal pain?
The symptoms that co-occur with abdominal pain can be a primary indicator of the condition responsible for a child’s digestive discomfort. For example, some children may experience fever, bloody stools, diarrhea, and even weight loss in addition to abdominal pain. These types of symptoms may indicate the presence of a particular illness and provide clues for diagnosis and treatment.
Are there any treatments for pediatric abdominal pain?
Most forms of pediatric abdominal pain – whether chronic or acute – are not caused by serious health issues. At our office, we always prefer to treat children with the most conservative treatment measures possible. This may include dietary changes and the use of over-the-counter medications when necessary. In fact, many cases of abdominal pain subside by eliminating lactose and processed foods, as well as by taking stool softeners when needed. Some children require greater medical interventions, including drug therapy and in some cases surgical intervention.