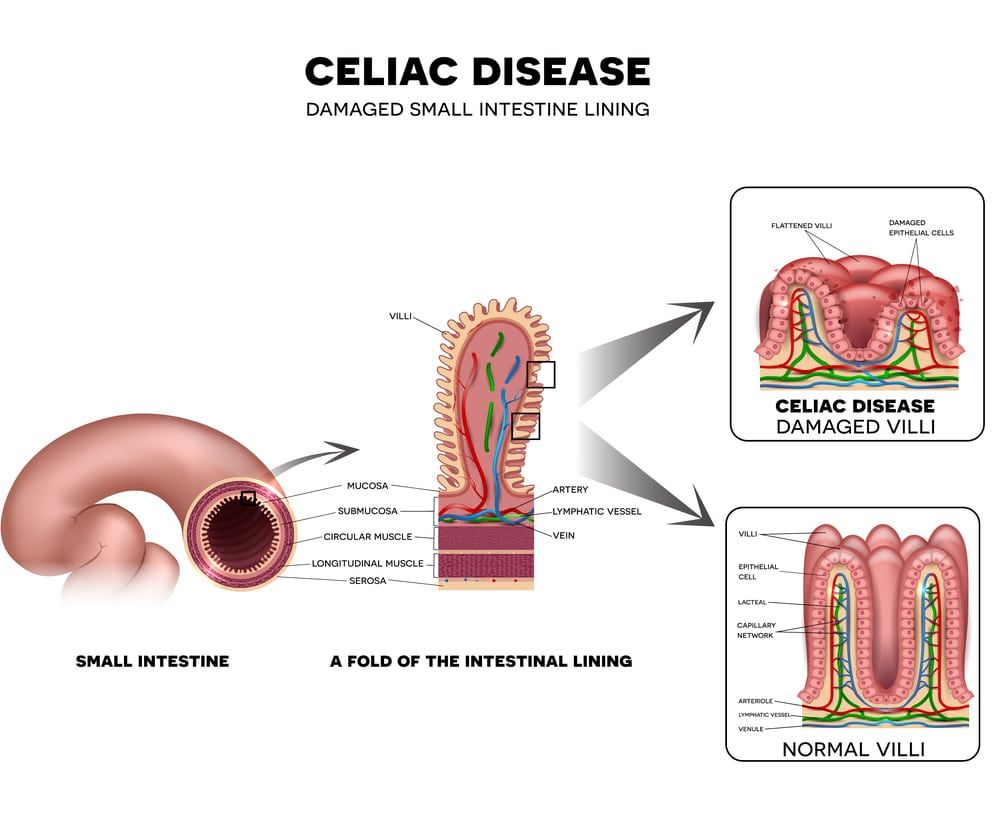
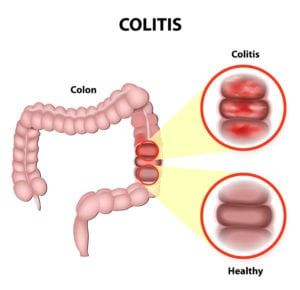
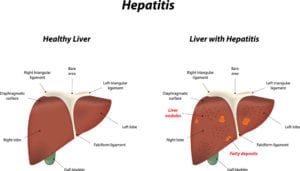
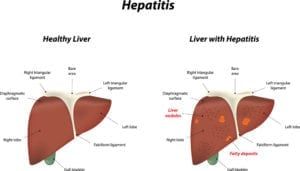
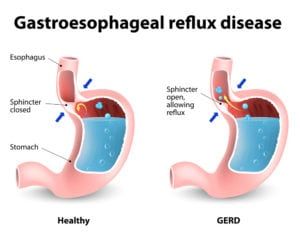
Celiac disease is an immune reaction gluten, a protein found in many everyday foods. Most children eat gluten on a daily basis with no intolerance or negative reaction. For children with celiac disease, even modest amounts of gluten can cause uncomfortable symptoms and trigger the immune system to begin attacking the inner lining of the small intestine. Over time, these reactions can break down the intestinal villi, preventing proper absorption of nutrients. If the disease is left unmanaged, a child with celiac disease can eventually develop nutritional deficiencies, as well as growth and development problems..
Did you know…
that celiac disease is increasing in prevalence among children – especially those with a family history of the condition? Currently, a child’s risk of developing celiac disease is 1 in 22 if he or she has a mother, father or sibling with the disease. Most children diagnosed with celiac disease receive their diagnosis at a young age – typically between ages 6 months and 2 years old, as this is the time when most children begin consuming foods with gluten.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of celiac disease in children?
The symptoms of celiac disease children can vary depending on the severity of the disease. However, some of the most common symptoms include abdominal cramping, bloating and diarrhea. Some children may also suffer a loss of appetite and weight loss.
How will a pediatric gastroenterologist diagnose celiac disease in my child?
Our staff is highly trained and experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric celiac disease. A review of your child’s symptoms and abnormal blood tests are often the first sign a child is suffering from celiac. We may confirm the diagnosis with additional testing, such as an upper endoscopy.
What are the treatments for celiac disease?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for celiac disease. However, many children can live normal, healthy lives by adopting gluten-free diets. Since gluten is found in wheat, rye and barley, these components must be removed from a child’s diet. However, there are many companies that produce breads, pastas and other foods without gluten, which can make the transition to a gluten-free diet much easier.