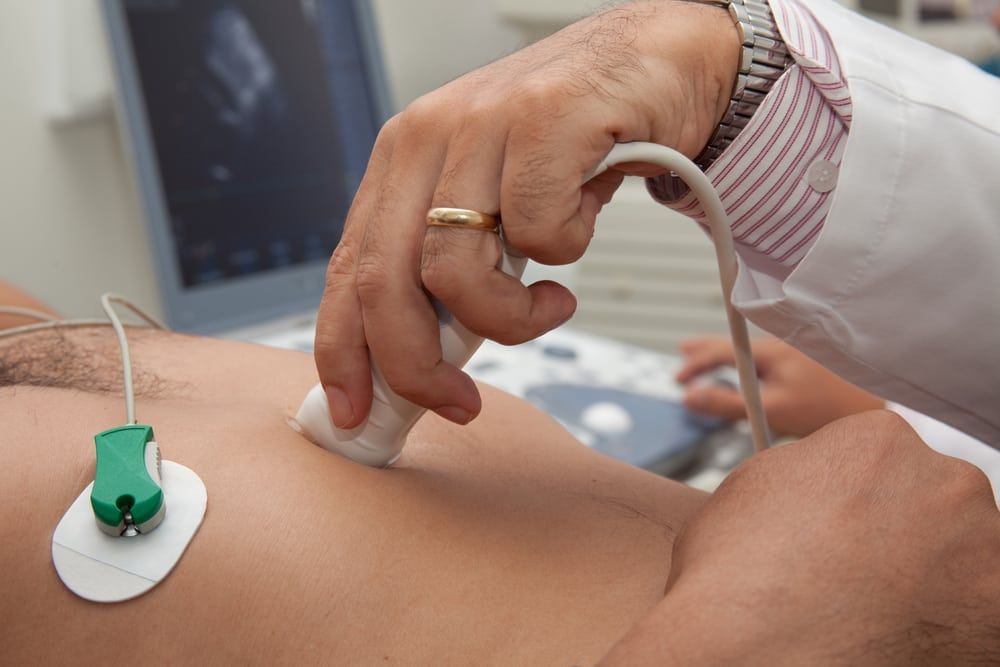
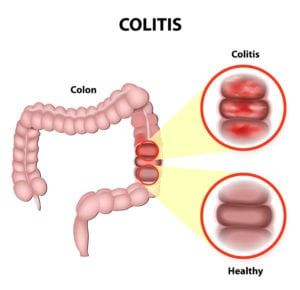
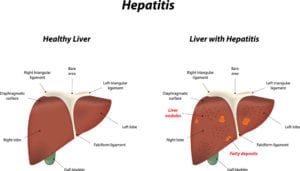
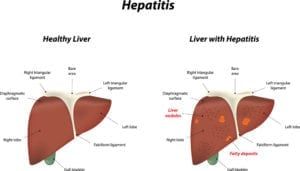
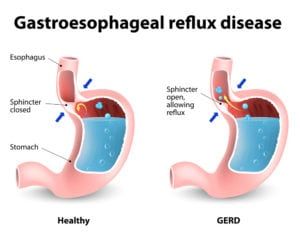
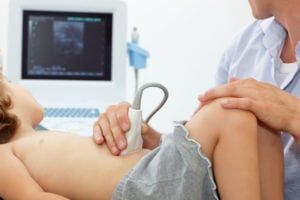
Echocardiography – also referred to as an echocardiogram – is a medical procedure used to measure the size and shape of the heart, as monitor the flow of blood through its valves and chambers. The diagnostic tests are more easily interpreted as a heart sonogram, which uses sound waves to measure cardiac output. Cardiologists often order echocardiograms to diagnose or monitor conditions like atrial fibrillation, congenital heart disease, heart infections, murmurs, and the condition of the heart muscles following a heart attack.
Did you know…
that there are two ways of performing echocardiography? Most patients receive the standard echocardiogram, which is known as a trans-thoracic echo. This is the fastest and least invasive of the two tests, with sonograms acquired via a chest probe placed on the outside of the body. The other type of echocardiogram – a trans-esophageal echo – is performed with the probe positioned behind the heart on the inside of the body. Patients are sedated or placed under anesthetic as the probe is placed inside the esophagus. The benefit of trans-esophageal echocardiograms is that they provide in depth imaging of the heart that is not available with the standard test.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need an echocardiogram?
Only your doctor or cardiologist can determine whether you need an echocardiogram. However, you are more likely to require this type of testing if you have suffered a stroke or heart attack, or if your doctor suspects that you are suffering from other types of cardiovascular conditions, such as pulmonary hypertension or abnormal heart valves.
What should I expect during an echocardiogram?
Your experience will vary according to the type of echocardiography you are undergoing. You will not need to take any special steps to prepare for a standard test though you may be asked to avoid food and drink in the hours prior to a trans-esophageal echo. A sonographer will perform a standard test by placing a probe along your ribcage and upper abdomen. The procedure is painless, although some patients require an IV injection of contrast liquid in order to achieve a better image of the heart. If you are undergoing a trans-esophageal echo, your doctor will numb the back of your throat before placing the scope inside your esophagus. If necessary, you may be placed under conscious sedation to help you relax during the procedure.
Will I need to follow any special instructions following my echocardiogram?
Echocardiography is an outpatient procedure that requires little or no recovery time. However, patients who have a trans-esophageal echo may experience some minor throat discomfort following the test. Depending on the results of your procedure, your doctor may order additional testing or request that you return for subsequent echocardiograms periodically.