Recurrent Pneumonia and Respiratory Tract Infections
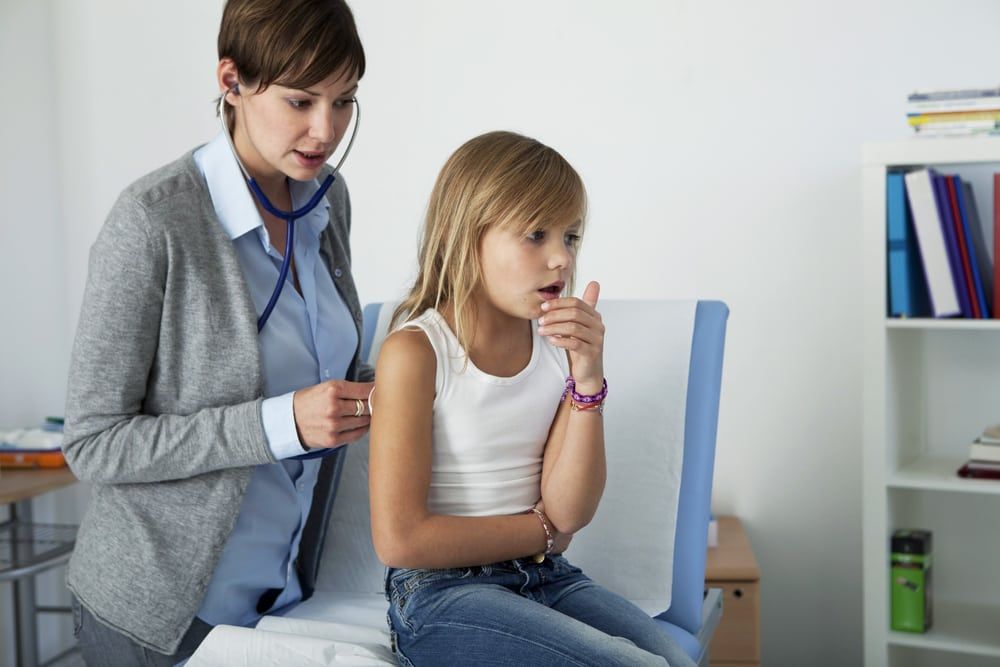
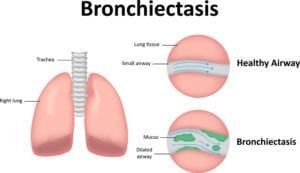
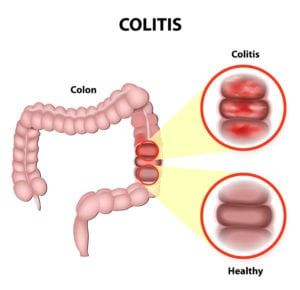
Nearly all children have respiratory infections from time to time, which are some of the most common causes of pediatric doctor and hospital visits. Usually, they are caused by viral infections or bacterial infections. However, some children develop recurrent infections, which may be a sign of an underlying pulmonary condition, such as bronchiectasis or COPD. Any child with recurrent pneumonia or other respiratory tract infections should see a pulmonologist to determine the cause of illness.
Did you know…
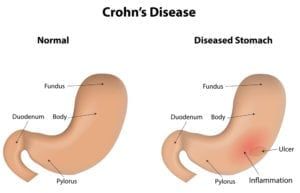
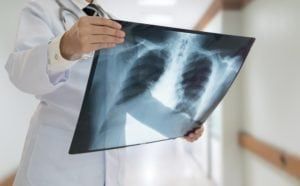
that most cases of recurrent pneumonia are diagnosed in children with a predisposing health condition? Recurrent pneumonia is recognized as two or more episodes of pneumonia in a 12-month period with x-ray confirmation of clearing in between. Symptoms of pneumonia may include fever, chills, body aches, and pain when breathing deep or coughing.
Frequently Asked Questions
When should my child see a pediatric pulmonologist for recurrent pneumonia or other respiratory tract infections?
Schedule a pulmonary appointment for your child if he or she has a recurring case of pneumonia or is frequently diagnosed with other respiratory infections, such as chronic bronchitis or sinusitis. Though recurrences of respiratory infections may be due to exposure to infectious agents, only a doctor can determine what types of steps should be taken to treat your child and prevent additional infection in the future.
Is there anything that increases my child’s risk of developing recurrent respiratory tract infections?
Recurrent infections may be caused by one or more of many different reasons. Some children are simply exposed to more than one virus, bacteria or fungi that results in illness. However, recurrent respiratory infections may also be more likely in children with certain conditions or risk factors, such as those with asthma, a weakened immune system or frequent exposure to second-hand smoke.
What are the treatments for recurrent pneumonia and respiratory tract infections?
The treatment for pneumonia and respiratory tract infections is often an antibiotic. These medications may also work on some forms of recurrent pneumonia. However, many cases of recurrent pneumonia and other types of respiratory infections may require anti-inflammatory medications, at-home care, and treatment for underlying health conditions.