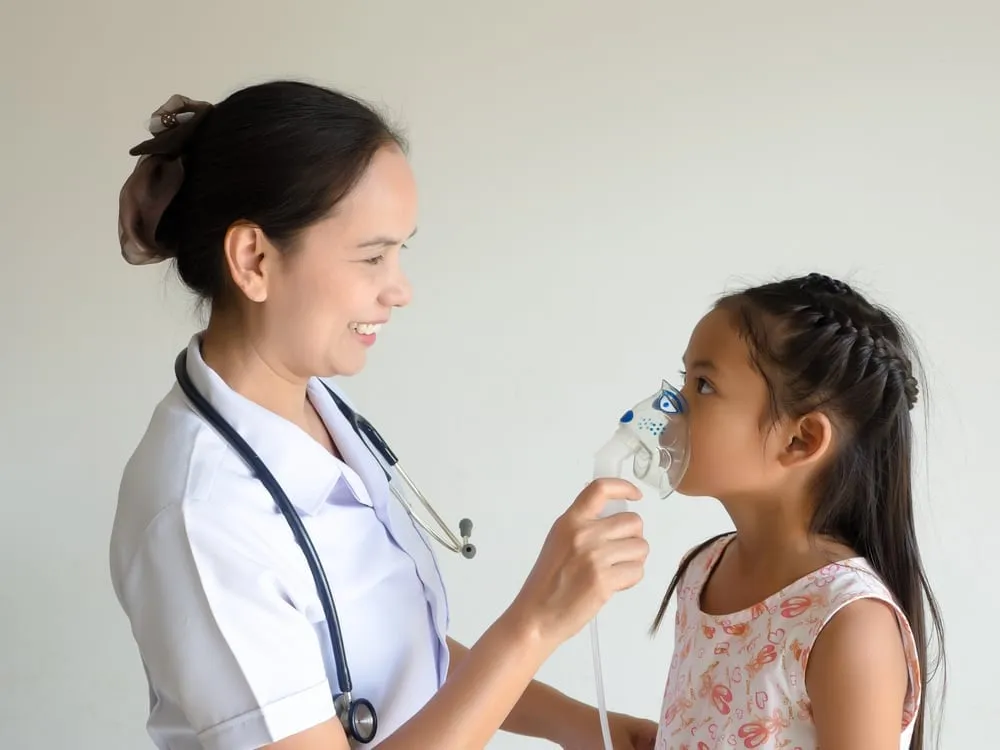
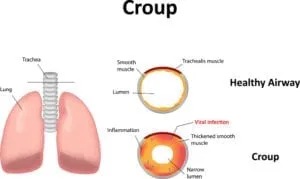
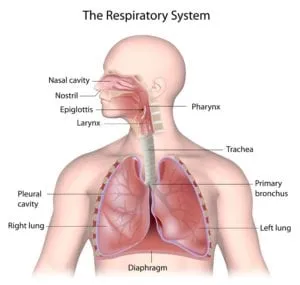
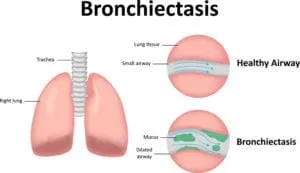
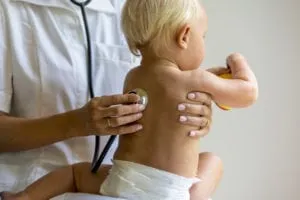
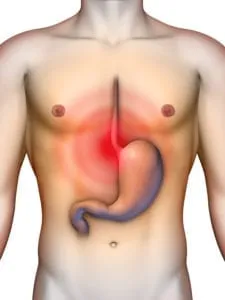
Wheezing is a sound produced by narrowed airways when breathing. As air passes through these constricted passages, it produces a high-pitched whistling sound. Wheezing can occur either when inhaling or exhaling though the latter is most common. A child who is wheezing is often experiencing difficulty breathing and may need to seek medical attention.
If your child is wheezing, you can help relieve his or her symptoms by placing your child in an area with warm, moist air. Many children find relief from wheezing after sitting in a steamy shower or sleeping in a room with a vaporizer. Drinking warm fluids may also be beneficial. Ensure that your children avoid exposure to tobacco smoke, which may worsen a wheezing cough.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes wheezing in children?
Wheezing can be a symptom of many different conditions, ranging from mild to severe? Some of the most common causes of wheezing in children include:
- Allergic reactions
- Asthma
- Aspirating on a foreign object
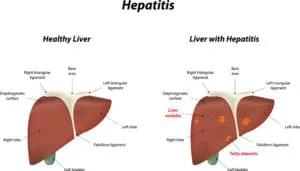
- Bronchitis
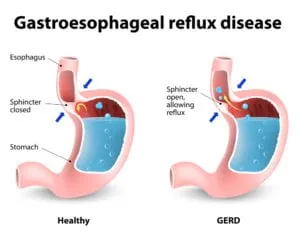
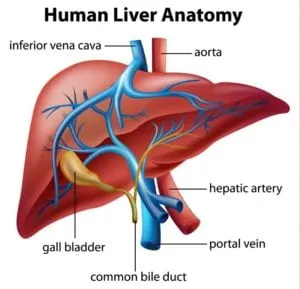
- GERD
- Pneumonia
- Viral Infections
How do I know if my child should see a pulmonologist about his or her wheezing?
Your child may need to see a doctor about wheezing if the condition appears for the first time or if it is recurrent without any explanation. Take your child to the nearest emergency room for wheezing caused by an allergic reaction or wheezing that is associated with shortness of breath, confusion or bluish skin.
What types of treatments are available for wheezing?
If your child is wheezing, a doctor may first check for blockages in your child’s airway. If your child has not swallowed any foreign objects, he or she may be able to relieve a wheezing cough by prescribing an inhaler. Efforts may also be made to treat or manage the underlying condition responsible for wheezing, which may help minimize symptoms. In some cases, further medical interventions may be necessary.