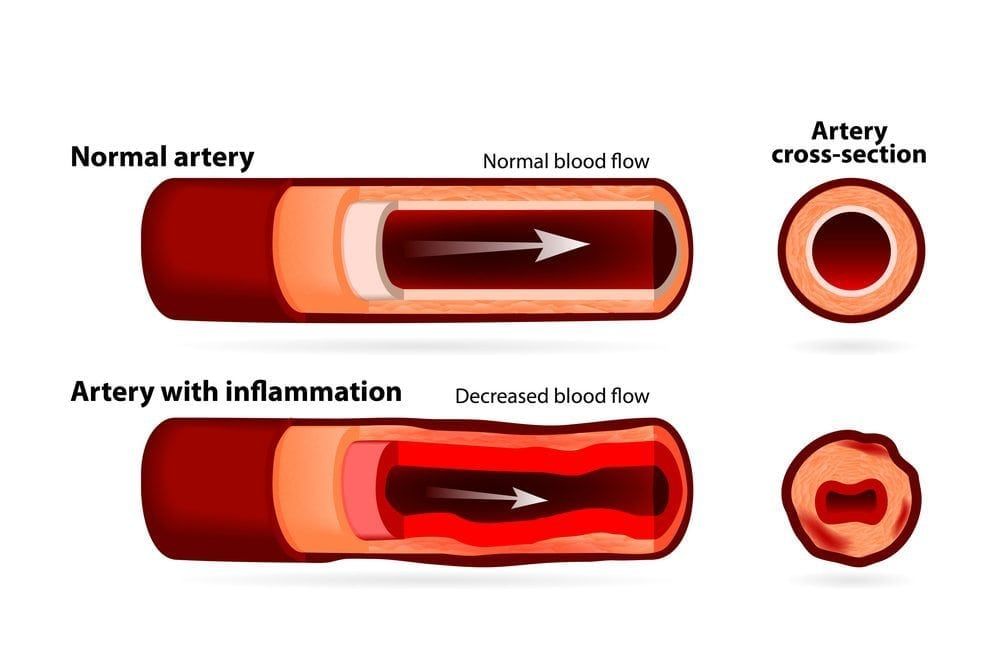
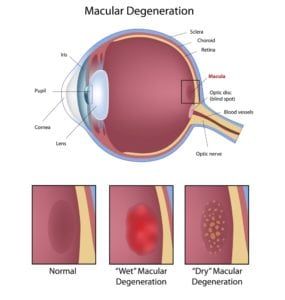
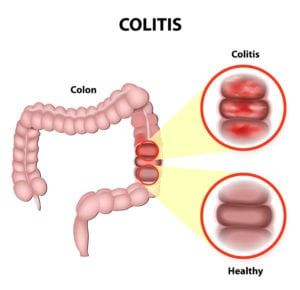
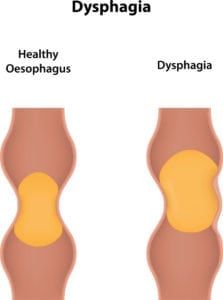
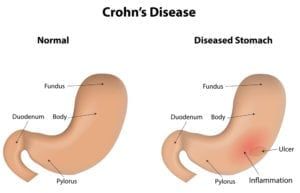
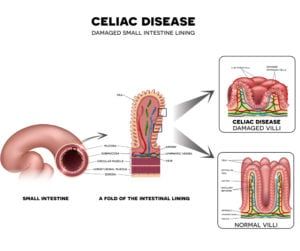
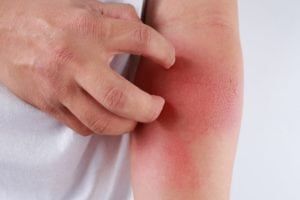
Vasculitis is an inflammatory disease that causes thickening of the blood vessel walls. Because there are several types of vasculitis, signs and symptoms can vary significantly from person to person. However, many people who suffer from this disease experience muscle and joint pain, as well as numbness and weakness. Some also experience fever, fatigue, and a loss of appetite that can lead to weight loss.
Did you know?
In some patients, vasculitis is acute and resolves after a short period of time. Others, however, suffer with vasculitis chronically and must undergo long-term vasculitis treatment to prevent organ and tissue damage. Vasculitis can occur on its own with no known cause or explanation, or it can occur as a secondary condition caused by an underlying medical condition, such as an infection or immune system disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
Could I be at risk for developing vasculitis?
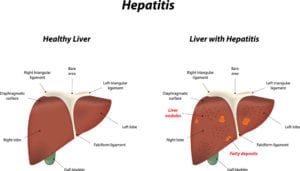
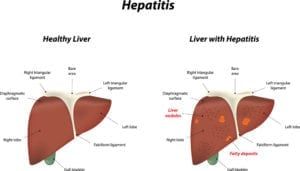
Anyone of any age or gender can develop vasculitis. However, certain people are at a higher risk for developing vasculitis than others. These include individuals who suffer from a pre-existing autoimmune condition, as well as individuals who have been diagnosed with a chronic condition, such as hepatitis B or C.
Do I need treatment for vasculitis?
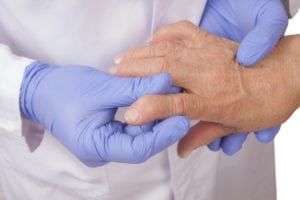
Though not all cases of vasculitis require medical intervention, many do. That is why it is important to seek the advice of a rheumatologist when experiencing the symptoms of this condition. Medications cannot cure vasculitis, but they can help reduce inflammation and suppress the areas of the immune system responsible for it.
Are there any steps I can take to prevent vasculitis?
No, there is no way to prevent vasculitis. However, in cases where vasculitis is caused by a medication, avoiding that medication may prevent future occurrences.